How Accessible Product Design Improves Business

Approximately 2.2 billion people all over the world suffer from visual impairments of varying severity, 5% of the world’s population experience hearing problems and 15% have disabilities. Therefore, when developing a software product, it is important to consider the accessibility of its design and inclusion. In this article, we’ll tell you how to put these principles into practice.
The importance of accessible design
A low-floor bus is accessible to users with disabilities. In the digital world, a similar rule applies: if a person with a physical or mental disability can use a service or application, such products are considered accessible.
Applications must be accessible to users who have hearing, visual or physiological impairments. In practice, this means, for example, providing subtitles to videos for the deaf, sign language translation functionality for the deaf-and-dumb, voice control for people who don’t have one or both hands. Accessible design helps people with disabilities to become full-fledged Internet users.
In 2006, the UN adopted the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, which accelerated the integration of people with disabilities into society. Since then, the principles of accessibility have been extended to the virtual environment. Microsoft is one of the world leaders in accessible design and its promoter. The company has created a guide for designers on how to develop better apps.
Another example of accessibility is Netflix. The interface of the platform has sufficient contrast so that the visually impaired can use it. Audio description allows the blind not only to listen to the dialogues in videos but also to imagine what is happening on the screen.
Users of services themselves began to pay attention to accessibility. In 2017-2019, about 3,000 lawsuits were filed against brands without accessible website design, including well-known Apple, Domino’s Pizza, etc.
Accessibility and inclusion
Design agencies focus on the average person: designers see a general portrait of the user and may not take into account the characteristics and needs of each person.
Accessible design focuses on a specific group or groups of users. Inclusive design, in its turn, is a broader concept. This approach means that a product solves the problems of different people in different life situations.
Proponents of inclusive design believe that people with different physiological abilities can, under certain circumstances, be in the same conditions. For example, both an elderly person and a child with a congenital illness can see poorly. Not only those who have lost a limb can use an application with one hand but also people who have been injured.
Microsoft has a special term for such consumers which is extreme users (brink users / extreme characters). By creating universal products, developers solve the issue of accessibility for a wide range of users. It turns out that subtitles designed for deaf people can also be useful for those with good hearing but in conditions of poor audibility.
Accessible and inclusive design helps companies to improve customer experience as customer focus is one of the defining factors of brand awareness.
How do you know that a site meets accessibility requirements?
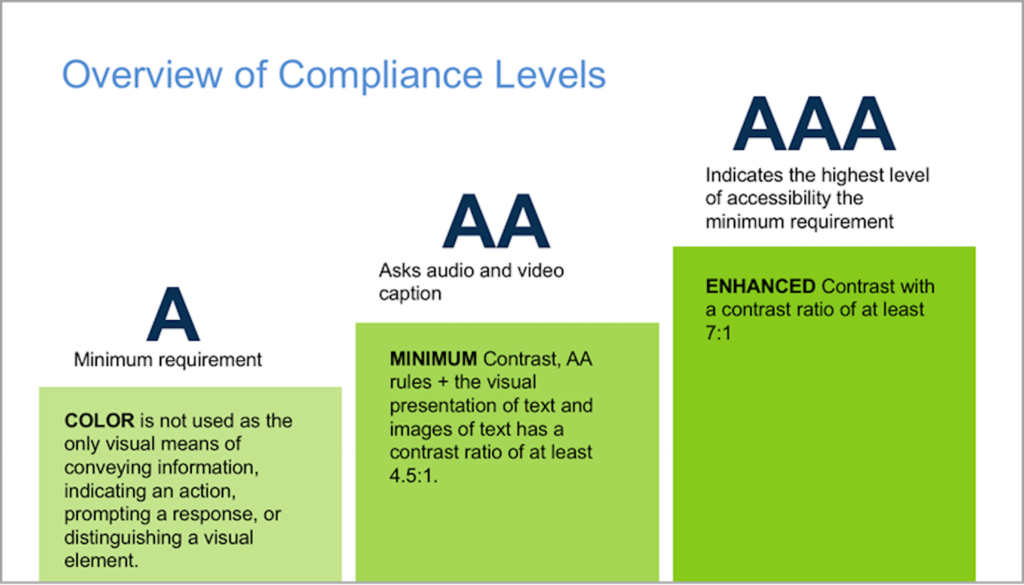
To create an accessible site, you should refer to the Web Content Accessibility Guideline (WCAG). The standard is built on twelve guiding principles for creating content at three levels – A, AA, and AAA.
- Level A
This is the minimum recommended level that can be implemented without a major redesign of an application. A software product must comply with 30 WCAG requirements: in particular, a text must be given an accessible name, labels are required for form fields, the application can be controlled using the keyboard, etc.
- Level ??
This is a more advanced level of the standard including 20 additional points. To implement AA requirements, you need to make changes to the product design: change the contrast, focus, adjust the status of messages, and so on.
- Level ???
This level summarizes the requirements of the previous levels and adds 28 serious conditions. Developers and designers must ensure that complex text has a simplified version, excludes embedded images, etc.
Let’s compare the levels based on one example. The contrast should be 4.4-3 for Level A, 6.9-4.5 for Level AA, and 21-7 for Level AAA.
The compliance of the site with accessibility parameters can be checked through WebAIM, Colourcontrast, Contrastchecker, Color Oracle, Wave, etc.
How to improve design accessibility
When implementing accessibility requirements, designers need to pay attention to the following issues:
- Color
The contrast between the text and background is of great importance for visually impaired people and for those whose eyes get tired from working at a computer.
The color of the text and buttons is significant for those who do not distinguish between colors (colorblindness) or see the world in black and white (monochromacy). For example, red and green warning messages can be misunderstood and should be provided with textual indicators: “Stop”, “Forward”, “Back”, “Resend”, etc.
Infographic 2:
- Font size and dimensions of elements
These characteristics are important for visually impaired people, the elderly, and users who are trying to read text from small smartphone screens. When choosing a font size, consider the semantic hierarchy of the elements on the page so that it is clear which element is the heading and which is a subheading. The size of the elements affects usability: small buttons are harder to click.
- Subtitles
Subtitles make it easier for deaf viewers and those in noisy environments to watch videos.
- Alternative text in graphics
By adding alternative text to photos, images, and icons, you will make it easier for blind people to use the app. A screen reader helps them to navigate the virtual world.
- Simplified text and navigation
Not all users perceive complex text in the same way. By adding a simplified version of the content to your site, you will help people with dyslexia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and low IQ to perceive information about your company, products, and services. Keyboard navigation is for users with limited mobility.
How to create products with accessible design
To make software design accessible:
- Let your teams know beforehand
While designers are responsible for this, both developers and testers should be aware of design issues to best implement the project with inclusiveness in mind.
- Conduct UX/UI research
UX/UI research helps to better understand your users. By conducting it, you will learn how people of different sex, ages, levels of physiological and mental development interact with the product. The study will show how effective your solution is and whether you are limiting your circle of users due to a lack of awareness.
Use accessibility assessment tools
When creating a custom web design, use the tools to assess the accessibility of the application:
- Color Oracle shows the site through the eyes of the colorblind and people with color vision deficiencies,
- Check My Colours evaluates the contrast of the color and background of pages,
- Wave evaluates the site’s HTML structure, contrasts, and compliance with the WCAG standard.
- Provide the same user experience for everyone
Compliance with the WCAG requirements does not always determine the convenience of a product for customers. For example, if subtitles are set up carelessly, users will not have time to read. An alternative solution is to invite visitors to choose the playback speed and transcript format themselves.
Accessibility as part of UI/UX design brings benefits in terms of business outcomes. By implementing the principles of inclusion, you will make software products more convenient, expand your audience, and improve your site’s SEO. If you want to create a product with accessible design, you should turn to an experienced software development company.