8 Ways to Optimize Your Google Smart Shopping Campaigns
Congratulations! You successfully set up your very first Google Smart Shopping campaign. After a month or two, you start to collect data and identify what demographics your products attract. You saw some really great results at first, but now they’ve started to plateau. Now what?
In this guide, we’ll walk you through eight optimization opportunities to take your shopping campaign to the next level. Keep reading to learn more!

Improve your SMB’s PPC performance with a FREE PPC audit.
Enter your website below:
Can you optimize a Google Smart Shopping campaign?
Short answer: Yes, though it may look different from a regular search campaign variation.
In a regular search campaign, you are given full control of the keywords you target, the ad copy you use, and the audiences you observe. You can optimize your campaigns with elements like:
- Ad variations
- Ad extensions
- Bidding strategies
A Google Smart Shopping campaign works a little differently. Online retailers submit product feeds containing product information. These feeds include things like product name, cost, shipping price, shipping weight, and even links to product images.
Since these listings come directly from a seller’s website, Google can show current and accurate pricing, offers, and product availability.
The structure of a Google Shopping Campaign
Before you launch your shopping campaign, connect your product feed from Google Merchant Center to your Google Ads account. Once connected, you’ll gain access to essential tools to use when diving into your shopping campaign:
Product groups
The product groups tab allows you to see the category of products you offer. When broken down, you can reflect on these group metrics in terms of impressions, clicks, and cost.
You can also determine how many of your products have been approved from your product feed and how many, if any, have been suspended or disapproved.
Products
The products tab allows you to see a list of all your products in your current Shopping feed and the status of each of those products. For example, if a product is sold out, Google will mark the product’s status as “Out of Stock.”
Therefore, integration between your Google Merchant Center account and your product feed is crucial to ensure it’s accurate. You can learn more about how to set up your GMC account here.
Placements
With placements, you exclude channels where your Shopping campaigns are less likely to provide your target return on ad spend (ROAS). If you find that most of your users access your site through desktop devices, for example, you can look into excluding placements like Apps.
Locations
Finally, an essential tool for navigating a successful Google Shopping campaign is location targeting. If your company only sells its products in the US, you’ll want to target sales made there.
This targeting is especially important for businesses that may not ship to certain states in the country. Providing this transparency is essential for Google to understand and trust your business.
8 optimizations to make to your Shopping Campaign
Now that you understand the tools you need to successfully manage your Shopping campaign, it’s time to dive into some optimization tactics. Here are eight optimization tactics you can use:
1. Optimize your product titles
When creating any page on the web, it’s essential to make the title of your page or product something that is relevant to user search intent. It’s one of the number one attributes Google looks for when determining the context of your products!
The attributes that you should include in your title depends on your industry. For example, when a user searches for a refrigerator, they’re not typically searching for “buy refrigerator.”
This broad keyword leads to a variety of different intents. When a well-informed user searches for a refrigerator, they may search for “buy a (brand) (size) (style) refrigerator.” There is a very specific intent involved with these searches.
Because Google Shopping campaigns do not allow you to create ad copy or ad variations, optimizing the titles of your products is the best way to help Google lead high-quality users to your product line.
2. Optimize your product description
Like product title optimization, your product description is an important tool for Google to show your Shopping ads to high-quality leads. Google will display a product description to the shopper, directly below your product title.
Just like your product titles, Google crawls your product descriptions for relevant keywords. It’s the perfect opportunity for you to insert any secondary keywords that might not have fit in your product titles.
Be sure to not keyword stuff. Provide each product with thoughtful, detailed content without including fluff for the sake of keyword optimization.
3. Choose the right product images
Your product’s images are the very first thing that shoppers see when they view your Shopping ads. There are a few guidelines to follow to ensure that Google approves your images and help your products standout amongst the competition:
- High-quality images: Ensure that your product photos are not blurry. Images must be responsive for mobile devices.
- Consistency: Your description, product title, and other elements should align with the picture you’ve selected. For example, if you’re selling a red t-shirt, the picture should be of a red t-shirt!
- Text overlay: Any images that are found to contain watermarks, promotional text, or manufacturer part numbers will be disapproved.
You can test both product and lifestyle images to determine which images work best to reach your target audience.
4. Optimize your product categories
There are many elements required to run a successful Google Shopping campaign. All this information helps Google better understand your business and works hard to show your ads to the right audience. One essential way to assist in Google’s process is to add product category information to your feed.
The ‘product_category’ element is a required part of your Google Shopping feed. Categories must be selected from Google’s list of product taxonomy.
There are over 6000 categories and subcategories to choose from! This product category information will not be displayed to shoppers. This information is a backend attribute that Google takes into consideration when populating the search results.
When selecting a product category, be mindful that the more specific you can make your subcategories, the more specific search intent Google can identify. In other words:
Animals & Pet Supplies > Pet Supplies > Dog Supplies > Dog Beds
Will give you a much more specific search intent than,
Animals & Pet Supplies > Pet Supplies
5. Subcategorize your feed to prioritize top-performers
One of the most valuable optimizations you can make when managing a shopping campaign is prioritizing the products that will give you the greatest return on investment (ROI). Visit your Google Shopping campaign in Google Ads, then select your main ad group. You’re then given the opportunity to Add Subdivisions by selecting the + button next to your ad group name.
You can then break up your product feed into the following categories:
- Category
- Product type
- Brand
- Item ID
- Channel
- Condition
- Or even create a custom label!
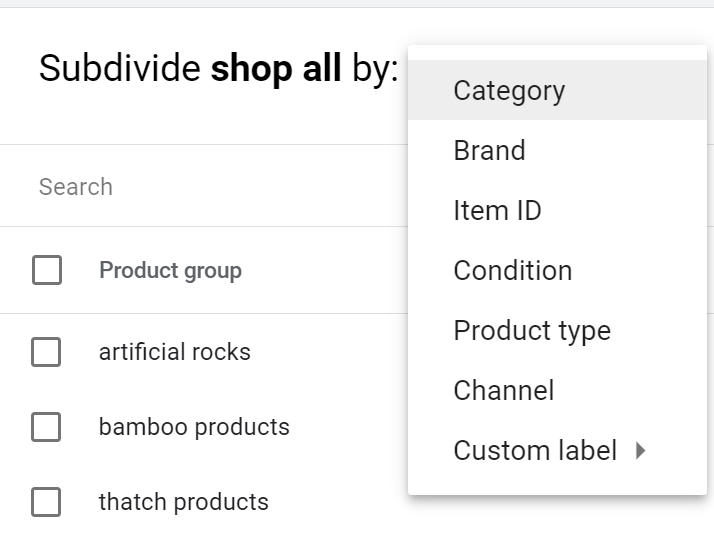
For example, say you operate a clothing store that offers women’s, men’s, and children’s clothing. If you find that you’re getting a higher ROI on children’s clothing ads, you may decide to create a subdivision for each product type and pause women and men ads to put more of your budget into your top-performer. Another opportunity is to focus on one specific product.
If one of the dresses you sell online produces exceptionally higher sales than other options, you may create a subdivision for Item ID to set a bid adjustment for that specific product.
This option is a great way to ensure that Google is pushing more users to the pages and products you want users to visit. We recommend that you wait to create subdivisions until you’ve allowed Google 2-3 months of time to collect data on your entire product feed.
6. Set placement exclusions
Another report to keep an eye out for when optimizing your Google Shopping Campaign is placement exclusions. A placement report shows you where a shopper saw your ad. This may be through Google Shopping, Google partner websites, or apps.
It’s important to review this report on an ongoing basis to ensure that your ads are displayed on platforms that feel relevant to your shoppers or business.
One example may be if your store sells industrial machinery, but your report shows that your ads have been seen on children’s mobile apps. By excluding this placement, you can point Google toward a more qualified channel.
7. Use negative keywords
Negative keywords can help you make the most of your campaign and ad spend. Unlike with text ads, Shopping campaigns don’t identify the keywords that triggered your ads to show to shoppers. However, you can be proactive by limiting the low-quality queries your ads will show for by adding negative keywords.
Let’s say that your clothing store sells red, green, and blue t-shirts. Someone searching for a yellow t-shirt will probably not buy your products, but they may click on your ads. If this is a continuous issue, it could really hurt your budget!
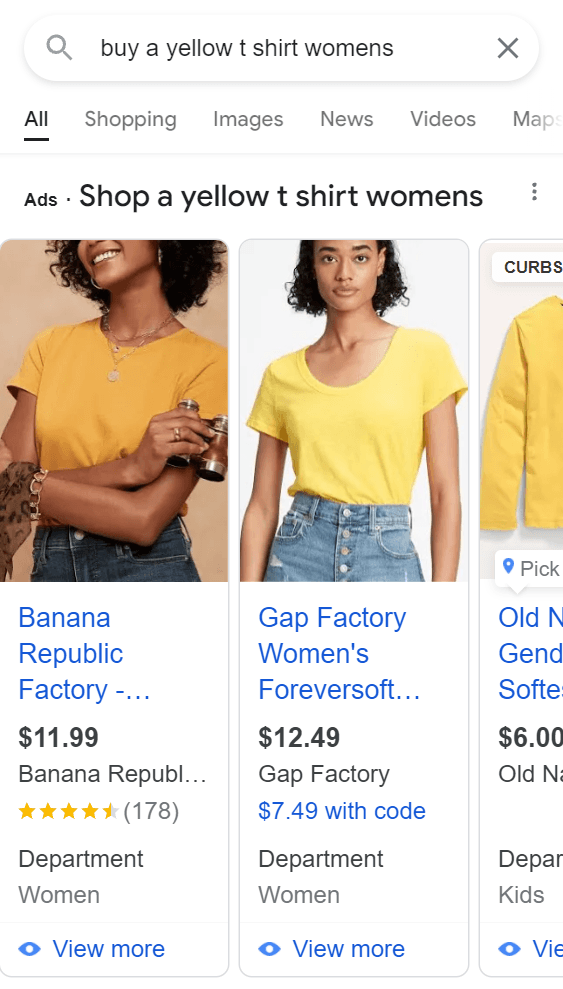
Adding a negative keyword for [yellow] would help prevent Google from showing your ads to lower-quality shoppers.
As the manager of your Google Shopping campaign, you can add negative keywords for the entire campaign or to each ad group separately.
8. Make bid adjustments
Using bid adjustments allows you to have more control over the type of user that sees your ad, where they see it, and when. There are three main demographics we’ll look at when setting bid adjustments: Schedule, devices, and location.
Schedule
An ad schedule refers to the time of day or day of the week that a shopper sees your ads. You may find that your ads are performing better on certain days of the week or at a specific time of day.
This data can be incredibly useful because you can better optimize your campaigns with cost per click (CPC) and cost per conversion in mind. You can set bid adjustments to favor the days/times that your ads are displayed.
Devices
It is essential to understand the way that shoppers see and convert through your ads. The Device report allows you to see how your users shop.
Let’s say that 70% of your traffic comes from mobile devices, 25% from desktops, and 5% from tablets. You can add a bid adjustment to favor the performance of your ads for mobile uses to get the most out of your budget.
Location
Geographic location also plays a huge role in the way we run and optimize shopping campaigns.
By using a location bid adjustment, you can favor the locations where you receive the most site traffic or where taxes/shipping rates are lower to really get the most of your ROAS. You can increase your bid for locations where increased sales are most important for you.
Why does optimizing your Google Smart Shopping Campaign matter?
You may wonder why these optimizations matter. After all, it is a smart campaign –– Google should have the knowledge to help bring your business to a positive ROI. While Google’s AI-Smart Learning is an incredible tool that you should continue to leverage, its algorithm can only take your business so far without providing some context.
The visibility of your ecommerce paid ad efforts depends on the thoroughness of your Google Shopping feed. The value you get out of it corresponds to the work you put into it. No matter who you are or what type of business you run, feed optimization is a must.
Get help launching Google Smart Shopping campaigns
Are you ready to sell some more products? It’s time to set up some campaigns and start optimizing your Google Shopping feed!
Need help launching your Google Smart Shopping campaigns? Our team of 450 marketing experts are ready to help you launch your ad strategy. Contact us online or call us today at 888-601-5359 to speak with a strategist!