How to Create a Minimum Viable Product: A Business Guide
Why does a business need an MVP?
Bringing a new application to market is always a business risk. About a third of startups fail because there is no demand for their products. To avoid this and not waste money, companies practice the development of a minimum viable product (MVP). This article will tell you what an MVP is and how to create it.
What is an MVP?
A minimum viable product is the first version of an application with a minimum set of basic features. It is ready for work and release to the market. This is a test version that helps to find out if a business understands the needs of its target audience correctly.
For example, when the Instagram MVP came out, users would log into the application, upload photos, apply filters, and share them with their friends. This social network has become popular from the start. The creators began to develop the program by adding new features: hashtags, live filters, stories, monetization tools, and so on.
The MVP concept was clearly illustrated by Henrik Kniberg, the author of Lean from the Trenches. He compared two product development processes: the traditional one and building an MVP.

In the traditional approach, a project team builds a product step by step. As a result, a business wastes time and money but customers may not like the final product.
With an MVP, things are different. A company focuses on the users’ problems and offers a solution. It enters the market. Customers use it and leave comments on its performance. Based on this feedback, the software development team improves the product and adds new useful features. Thus, after each such refinement, the product evolves.
In practice, it turns out like this: developers create a product within a month or two, implement the most important features, and invite users to test them. If the business idea is good and customers are willing to work with the application, the team continues to improve the software until it becomes a full-fledged digital product.
What are the benefits of an MVP for a business?
Companies start software development with an MVP to reap the following benefits:
Bringing an application to market faster. It will take developers only a few months to create an MVP. Then it enters the market and starts generating money that can be used to refine the product.
Attracting early adopters. An MVP introduces a business to the target audience. By researching it, the company learns what users like and what they expect from this software.
Getting valuable customer feedback and improving a product. An MVP is needed to check the number of users and buyers, the cost of customer acquisition, and so on. This data will be useful to improve the first version of a product.
Understanding if a product is suitable for the market. Software developers evaluate whether users like an application and whether it outperforms competitors’ offerings.
Getting started with minimal investment. The cost of developing an MVP is lower than that of the final software version as it includes only the main functions with which the program serves the target audience.
Attracting investors for the further development of a project. With the help of an MVP, it is easier for a business to demonstrate the merits of a product and get funding. When investors see that an idea works, they are more willing to invest in custom software development services.
How to build an MVP: a step-by-step guide
Companies often want to create a perfect product. As a result, the development of an MVP is delayed and the budget is running low. Other organizations, on the contrary, cut software functionality so severely that it becomes unsustainable.
Eric Ries, the author of The Lean Startup, has a simple piece of advice. After you come up with a product, you need to cut the functionality in half and repeat the same thing twice. It means that you should reduce the version by eight times.
An MVP development plan includes the following four steps:
Research the market
Eric Ries defined the main goal of startup projects: “The fundamental activity of a startup is to turn ideas into products, measure how customers respond, and then learn whether to pivot or persevere. All successful startup processes should be geared to accelerate that feedback loop.” For these purposes, you should conduct market research.
To create a relevant and useful product, project participants must know the purpose of the application, who will use it, what customer problems it will solve, and how exactly. By analyzing competitors, a business learns from their ideas and adds its own unique features, which makes the product stand out in the market.
Create a customer journey map
To create a useful program, you need to look at it from the point of view of customers and trace all the steps of users to the completion of purposeful action.
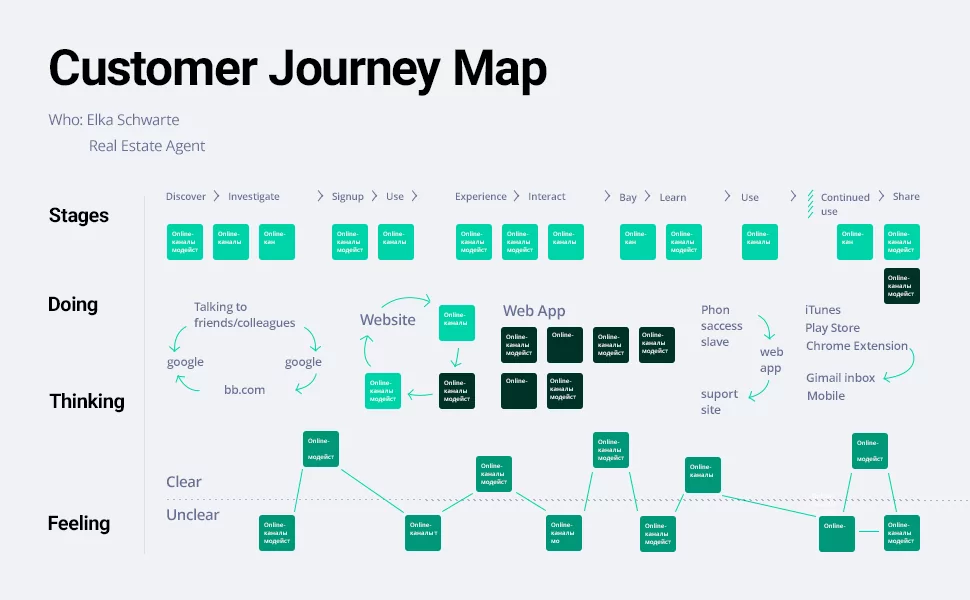
For the consumer journey map to be comprehensive, you need to do the following:
- Define user categories;
- Define user tasks, that is, actions that users need to perform to achieve their goals;
- Define the end of the user’s path, for example, “buy product”.
The map ensures that developers don’t miss anything when they create an MVP. As a result, clients will receive useful and up-to-date software.
Select the main features of the application
A customer journey map can help you determine which features to implement in your application. The software development team will prioritize functionality as low, medium, and high. The critical functions, without which the product cannot work, will be included in the MVP in the first place. For convenience, project teams use a priority matrix.

This is how a team providing custom software development services describes what features will be included in the first and subsequent versions of the product.
Develop and launch an MVP
When an MVP is released to the market, the software development team will constantly analyze customer feedback. It will tell you how to develop the product, what features to add to the software, what prevents users from achieving their final goals, whether there are errors, and so on.
An MVP may undergo several iterations before a useful competitive application is obtained.
Major mistakes of MVP development
Here are common mistakes of MVP development.
- Creating a product without researching the market. From a business perspective, a software product may be perfect. But if it fails to solve a consumer problem, it doesn’t make sense.
- Overloading an MVP or creating a feature deficit. An MVP includes the most necessary functions for the normal operation of an application. All other features can be added in future versions.
- Not prioritizing features. Working with an MVP does not stop at one release. For the software to develop consistently, you should plan what features will be implemented in each iteration.
Conclusion
An MVP helps to learn a lot about users and “test the water” before diving headfirst. All you need to do is plan your business hypothesis, define the core features of an MVP, understand your target audience, and find the right software development partner offering outsourced IT support. A team of professionals will help you build the most efficient solution.